3.2V Low-Voltage Power Architecture
Table of Contents
Part I — Executive Overview
The 3.2V Low-Voltage Architecture is designed to deliver high electrical efficiency, enhanced safety, and long service life for modern solar street lighting systems.
By matching the typical LED forward voltage range and using a 3.2V nominal LiFePO₄ battery, the system can reduce unnecessary voltage conversion, lowering thermal stress and improving reliability.
In practical engineering designs, this architecture can support 3 m to 12 m pole heights, especially when combined with:
- 230 lm/W ultra-high-efficiency LEDs
- Sunlurio Dual-Controller System (80W real output)
- LiFePO₄ Battery Packs (3.2V nominal)
- MPPT charging + smart load management
Note: Actual efficiency and output depend on driver topology, wiring design, component selection, operating temperature, and load strategy.
Part II — System Architecture Overview
Block Diagram — 3.2V Direct-Drive Solar Lighting System
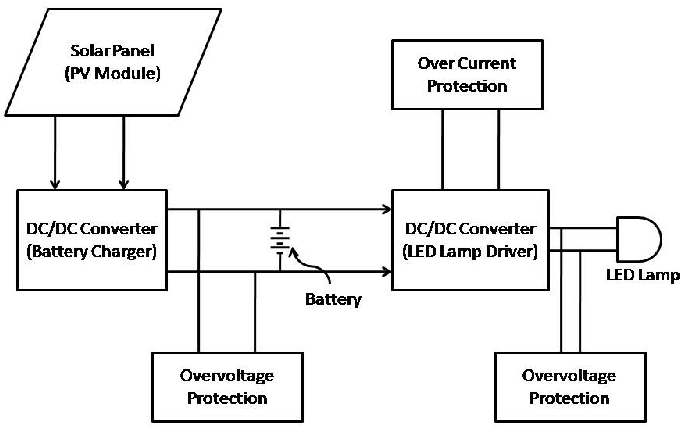
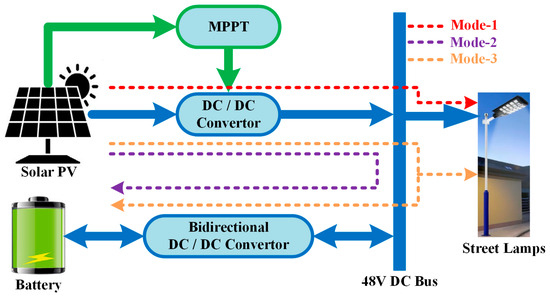
PV Module → MPPT Controller → 3.2V LiFePO₄ Battery → LED Driver → LED Module
↘ IoT / Sensors / Communication
Part III — Engineering Rationale
3.2V = Native Match for LED Forward Voltage
- White LED forward voltage (typical): 2.7–3.3V
- LiFePO₄ battery voltage (nominal): 3.2V
Result: fewer boost/buck steps → lower losses → less heat → longer lifetime potential.
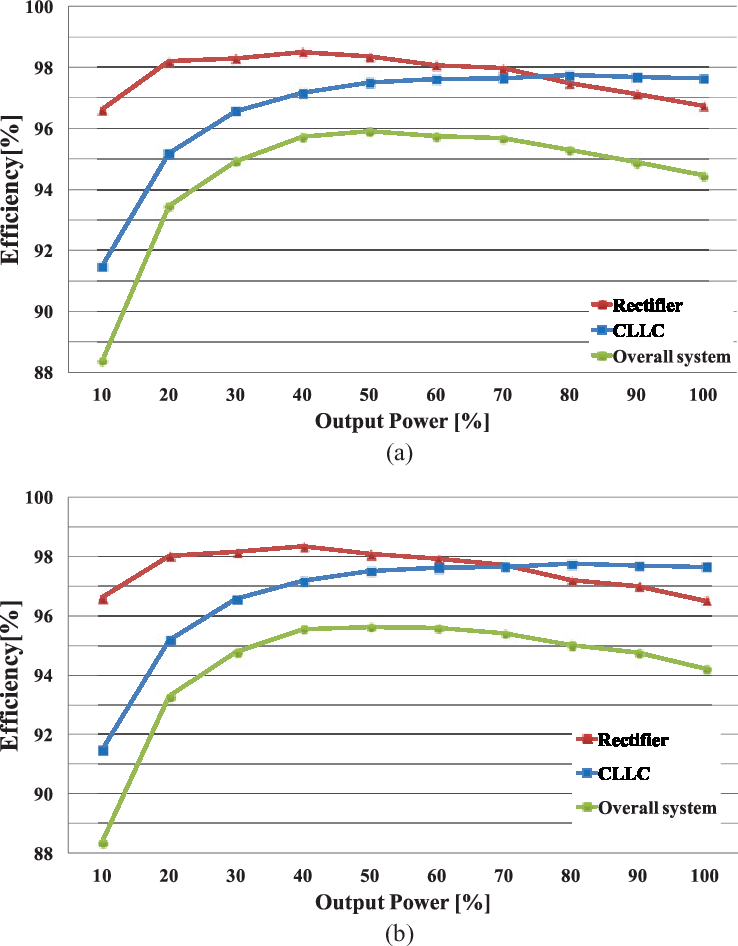
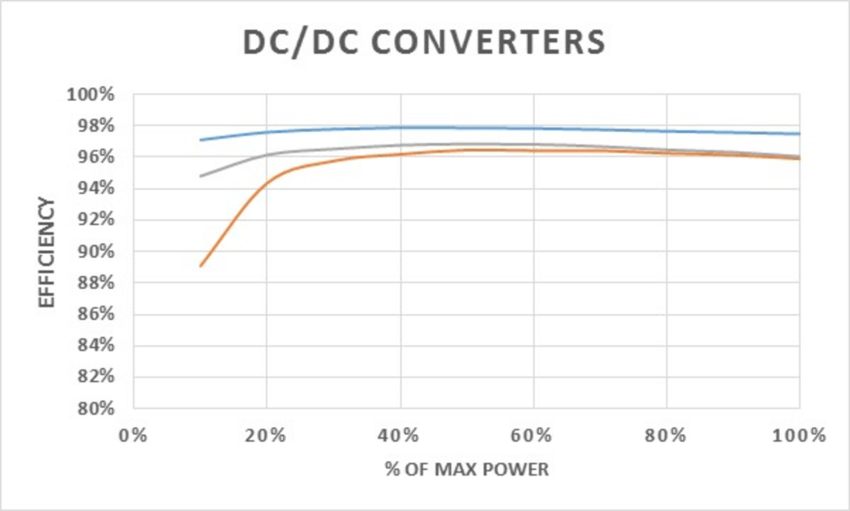
System Efficiency Comparison (Typical Range)
| Architecture | Conversion Path | Driver/Conversion Efficiency | Total System Efficiency* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2V | None (direct-drive oriented) | 95–98% | 95–98% |
| 12.8V | Buck → LED | 90–93% | 85–88% |
| 24V | Buck → LED | 85–90% | 80–85% |
*Total system efficiency here is a practical engineering estimate that depends on controller losses, wiring loss, and driver design.
Efficiency Visualization: (Diagram Placeholder)
Part IV — Safety & Compliance Framework
SELV Safety Compliance (IEC 60364-4-41)
3.2V is far below hazardous DC voltage thresholds, enabling SELV-oriented safety design and reduced electric shock risk.
Battery Compliance (Common References)
- IEC 62133-2
- IEC 62619
- UN38.3
- MSDS
- UL1642 (optional / project-dependent)
BMS Required Protections
- Overcharge
- Overdischarge
- Overcurrent
- Short circuit
- Temperature cutoff
- Cell balancing
LED & Driver Compliance (Common References)
- IEC 60598-1 / IEC 60598-2-3
- IEC 61347-1 / IEC 61347-2-13
- LM-79 / LM-80 / TM-21
Part V — Electrical Engineering Analysis
Voltage Drop (IEC 60364-5-52)
Formula: Vdrop = I × R × L
Typical street light parameters:
- I = 1.2–2.8 A
- L = 1.2 m
- R (0.75 mm²) = 0.024 Ω/m
Estimated: Vdrop ≈ 0.08 V (≈ 2.5%) < 3% limit
Thermal Advantages
- Reduced or minimized DC-DC conversion loss
- Reduced switching heat
- Lower MOSFET stress
- Potentially longer lifetime and higher stability
Part VI — Photometric & Performance Modeling
LED Baseline
Formula: Φ = P × ηLED
Example (Sunlurio reference configuration): 80 W × 230 lm/W = 18,400 lm
Illuminance Prediction for 3–12m Pole Height
Table — Predicted Average Illuminance (80W, 230 lm/W)
| Height | Beam Diameter | UF | Avg Illuminance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 m | 6–7 m | 0.55 | 265–330 lux |
| 4 m | 8–9 m | 0.55 | 158–203 lux |
| 5 m | 10–11 m | 0.50 | 97–118 lux |
| 6 m | 12–13 m | 0.48 | 67–78 lux |
| 7 m | 14–15 m | 0.45 | 47–54 lux |
| 8 m | 16–17 m | 0.43 | 36–39 lux |
| 9 m | 18–19 m | 0.40 | 26–29 lux |
| 10 m | 20–21 m | 0.38 | 20–22 lux |
| 11 m | 22–23 m | 0.36 | 16–17 lux |
| 12 m | 24–25 m | 0.35 | 13–14 lux |
Illuminance vs Height Curve: (Diagram Placeholder)
Part VII — Application Suitability
| Application Type | Recommended Height | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Rural / Village | 3–6 m | Excellent |
| Urban Community | 6–9 m | Excellent |
| City Secondary Roads | 8–10 m | Excellent |
| Main Roads | 10–12 m | Good |
| Industrial Areas | 7–9 m | Excellent |
Part VIII — Mechanical & Installation Requirements
- Pole: Q235/Q345 steel, hot-dip galvanized
- Battery: LiFePO₄, IEC 62133-2 compliant
- Controller enclosure: IP65
- SPD: ≥ 10kA
- Wiring: ≥ 0.75 mm²
Part IX — Procurement Guidelines
Documents Required
- LM-79 Report
- LM-80 + TM-21
- IEC 62133-2
- UN38.3
- Controller schematic
- Mechanical drawings
Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT)
- Open-circuit voltage
- Load test
- Thermal test
- Charging curve verification
- Runtime testing
Part X — Final Engineering Conclusion
When properly engineered, Sunlurio 3.2V architecture + 230 lm/W LED + Dual Controller (80W real output) can deliver:
- High system efficiency (typically 95–98% in direct-drive oriented designs)
- Reduced conversion loss and thermal stress
- Strong alignment with LED forward voltage
- SELV-oriented safety design
- Strong performance coverage across 3–12 m solar street lighting projects
This architecture is positioned as a highly competitive electrical foundation for modern solar street lighting systems, especially where efficiency, safety, and long-life operation are procurement priorities.
Author introduction







