Street lights play a critical role in urban infrastructure, ensuring safety and visibility at night. Modern street lighting systems rely on automation for efficiency and convenience. But how exactly do they work?
Street lights operate through automated control systems, which can be time-based, sensor-driven, or remotely managed. Electrical circuits ensure stable voltage and current supply, while wiring configurations impact efficiency and reliability. Smart innovations continue to improve street lighting for energy savings and adaptive functionality.
Understanding how street lights function requires exploring their control mechanisms, electrical properties, wiring design, and future trends.
How Are Street Lights Controlled?
Street lights are controlled through timing schedules, light sensors, remote systems, and smart networks. Each method optimizes efficiency and ensures proper illumination.
Primary Control Methods
| Control Method | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Timing Control | Uses pre-set schedules to switch lights on/off | Simple and cost-effective |
| Remote Control | Allows manual operation via mobile apps or centralized systems | Provides flexibility and instant adjustments |
| Light Control Sensor | Adjusts brightness based on ambient light levels | Automatically adapts to changing conditions |
| Network Control | Integrates smart street lighting into a central system | Enables real-time monitoring and remote diagnostics |
Common Street Light Control Systems
| System Type | Description | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Light Sensors + Timing Control | A combination of scheduled operation and sensor-based adjustment | Higher initial cost but more energy-efficient |
| Traditional Systems | Basic manual or pre-set timing control | Lacks adaptability to real-time conditions |
| Smart Street Lighting | Uses IoT, sensors, and AI to optimize lighting | Requires network infrastructure and maintenance |
Future trends in street lighting control focus on increasing sensor-based intelligence, allowing dynamic adjustments for better efficiency and sustainability.
Electrical Features of Street Lights
Street lights operate on specific voltage standards and consume regulated amounts of current to ensure stable and efficient operation.
Voltage Standards for Street Lights
| Region | Voltage Standard | Description |
|---|---|---|
| United States & Canada | 120V AC | Common for residential and commercial lighting |
| Europe & Other Regions | 220V - 240V AC | Standard for higher efficiency in street lighting |
| Voltage Regulation | Uses transformers and stabilizers | Ensures a stable power supply for uniform brightness |
Current Consumption of Street Lights
| Factor | Range | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Current Consumption | 0.1A (100mA) - 1A | Varies based on the lamp type and brightness settings |
| Power Efficiency | High voltage, low current | Reduces energy loss and increases lifespan |
Street lights are designed to minimize power consumption while providing adequate brightness for safety and visibility.
Wiring & Circuit Design of Street Lights
The wiring and circuit design of street lights determine their reliability and maintenance ease. Parallel wiring is the preferred method for ensuring consistent performance.
Parallel vs. Series Wiring
| Wiring Type | Function | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel Wiring | Connects all lights directly to the power source | Ensures each light receives equal voltage and remains functional even if others fail |
| Series Wiring | Links lights in a single circuit | If one light fails, the entire circuit is disrupted |
Parallel wiring is widely used due to its reliability, consistent brightness, and ease of maintenance.
How Are Street Lights Wired?
| Step | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Planning | Determine street light locations based on road layout | Ensures optimal illumination |
| 2. Laying Electrical Conduits | Install underground or overhead power lines | Connects lights to the power grid |
| 3. Connecting LED Circuit | Link LED modules to the power source | Enables electricity flow for illumination |
| 4. Debugging & Testing | Check for wiring faults and performance | Ensures proper operation before activation |
Proper circuit design is crucial for maintaining street light efficiency and minimizing power loss.
Future Innovations in Street Lighting
Smart technology is transforming street lighting with automation, adaptive brightness, and renewable energy integration.
| Innovation | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Street Lights | Uses IoT for remote monitoring and control | Improves maintenance efficiency and reduces downtime |
| Adaptive Lighting | Adjusts brightness based on traffic, weather, and pedestrian activity | Enhances energy efficiency and safety |
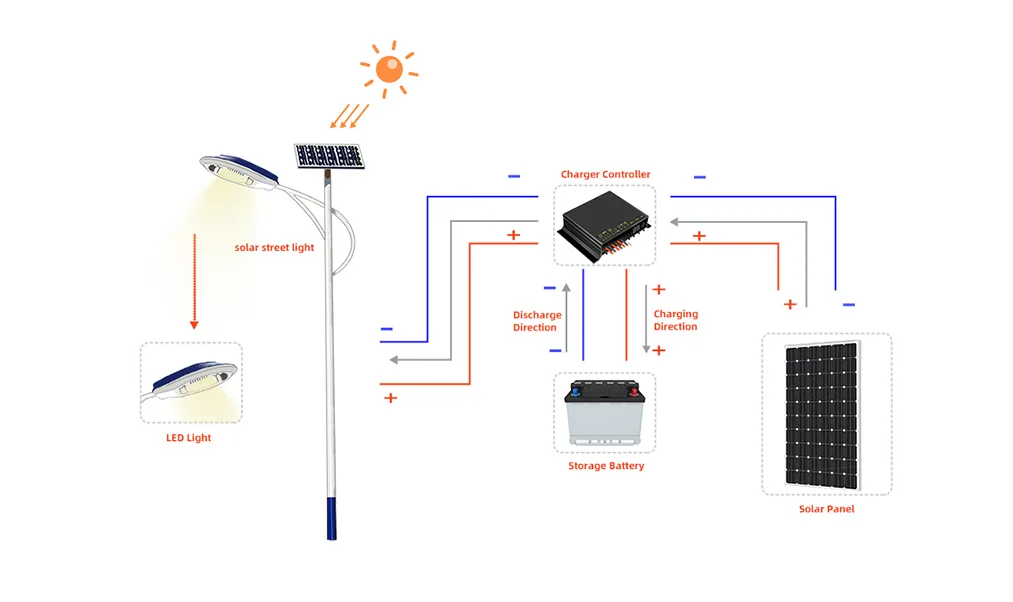
| Solar-Powered Street Lights | Hybrid models with solar panels and grid power | Reduces reliance on traditional energy sources |
Future street lighting systems will continue to evolve, offering smarter, more efficient, and environmentally friendly solutions.
Conclusion
Street lights function through automated control mechanisms, stable electrical properties, and efficient wiring configurations. As technology advances, smart and adaptive lighting will become the norm, optimizing energy use and improving urban safety. The future of street lighting lies in sensor-based and network-controlled solutions, making cities smarter and more sustainable.