Are you unsure whether hot-dip or cold galvanizing is the right choice for your light poles? Selecting the wrong galvanizing process can lead to corrosion, high maintenance costs, and reduced lifespan, especially in harsh environments.
Hot-dip galvanizing provides superior corrosion resistance, durability, and low maintenance for outdoor environments, while cold galvanizing is cost-effective and suitable for dry, indoor settings. Understanding their differences ensures the right choice for your light poles.
Let’s explore both processes in detail and help you make an informed decision.
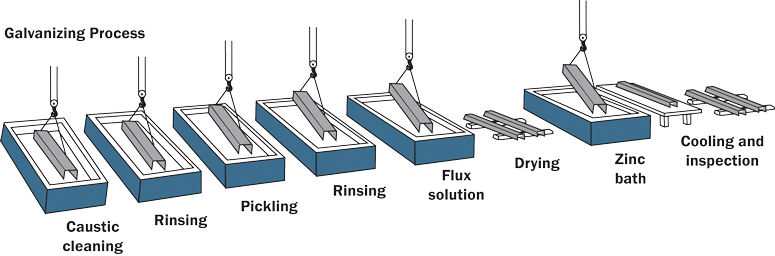
What is Hot-Dip Galvanizing?
Hot-dip galvanizing involves immersing steel light poles into molten zinc, creating a thick, robust zinc layer that bonds metallurgically to the surface.
Key Features:
- Thick Zinc Coating: Typically 65–120 microns, offering excellent corrosion protection.
- Durability: The zinc layer resists mechanical damage and environmental wear.
- Extended Lifespan: Can last 20–50 years with minimal maintenance.
- Matte Silver Appearance: Provides a slightly textured, industrial finish.
Best Applications:
- Coastal Areas: High humidity and salt exposure demand the superior corrosion resistance of hot-dip galvanizing.
- High Pollution Zones: Industrial areas with harsh chemical exposure.
- Municipal Lighting: Long-lasting protection reduces long-term costs for public projects.
What is Cold Galvanizing?
Cold galvanizing, also known as zinc-rich coating, applies a thin layer of zinc to the light pole surface using an electroplating process.
Key Features:
- Thin Zinc Coating: Typically 5–15 microns, less protective than hot-dip galvanizing.
- Smoother Finish: Offers a polished, shiny appearance.
- Shorter Lifespan: Usually 5–10 years, requiring more frequent maintenance.
- Lower Initial Cost: Ideal for projects with tight budgets.
Best Applications:
- Indoor Settings: Dry, controlled environments where corrosion risk is low.
- Temporary Structures: Short-term use poles or equipment.
- Budget-Sensitive Projects: When cost takes priority over long-term durability.

Key Differences Between Hot-Dip and Cold Galvanizing
| Feature | Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Cold Galvanizing |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, withstands harsh outdoor environments. | Moderate, suitable for mild conditions. |
| Durability | Long-lasting (20–50 years). | Shorter lifespan (5–10 years). |
| Coating Thickness | 65–120 microns. | 5–15 microns. |
| Appearance | Matte silver with a textured finish. | Shiny, smooth surface. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower maintenance. | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance. |
| Best Use Cases | Outdoor, industrial, and coastal settings. | Indoor and temporary setups. |
How to Choose the Right Galvanizing Process for Light Poles
1. Assess the Environment:
- Harsh Outdoor Conditions: Opt for hot-dip galvanizing to ensure long-lasting protection against corrosion.
- Indoor or Dry Areas: Cold galvanizing may suffice for low-risk environments.
2. Consider Longevity Needs:
- For projects requiring minimal maintenance and decades of durability, hot-dip galvanizing is the superior choice.
3. Balance Budget and Performance:
- If budget constraints are a primary concern and the poles are not exposed to harsh conditions, cold galvanizing is a more economical option.
4. Consult a Professional:
- Every project is unique. Seek advice from a trusted manufacturer to determine the best solution for your specific needs.

Conclusion: Ensuring Long-Term Performance with the Right Galvanizing Process
The choice between hot-dip and cold galvanizing depends on the environment, budget, and durability requirements of your project. Hot-dip galvanizing excels in outdoor and industrial settings, offering unmatched corrosion resistance and a long lifespan. Cold galvanizing is suitable for less demanding conditions, providing an affordable alternative for indoor or temporary applications.
Need expert advice on galvanizing your light poles? Consult with a trusted manufacturer to ensure your poles perform beautifully and reliably for years to come.


