Street lighting control systems are essential for enhancing energy efficiency, reducing unnecessary lighting, and enabling intelligent management of public lighting infrastructure. These systems offer various features like automated switching, dimming, and real-time monitoring, helping to reduce energy consumption and operational costs significantly.
From photocell switches to advanced smart systems, each control method offers unique benefits to optimize streetlight performance and sustainability.
This guide explores various types of control systems, their functions, and the benefits they bring to modern street lighting projects.
What We Can Get from the Street Light Control System
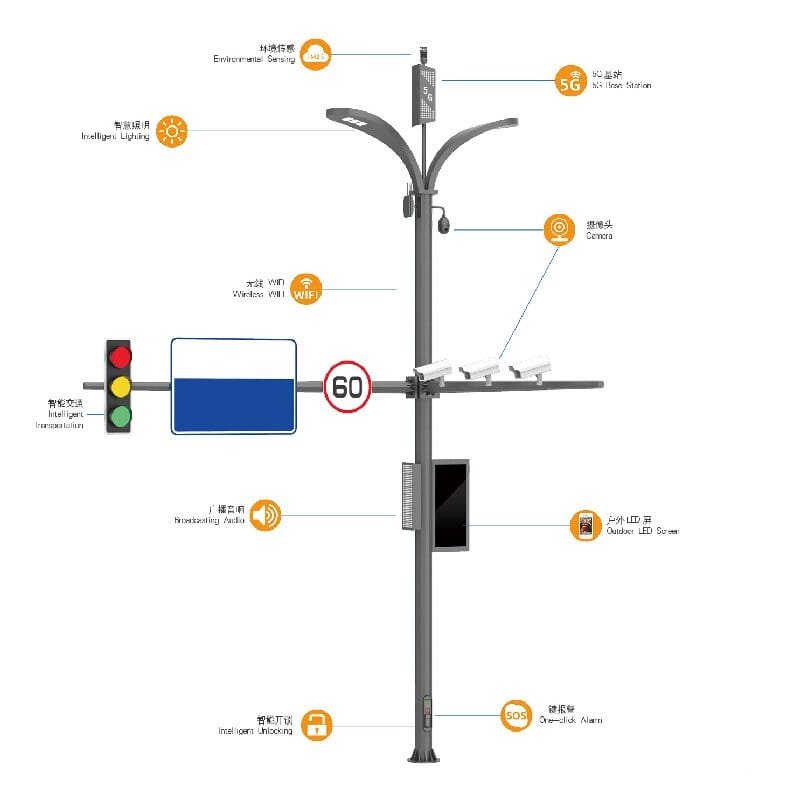
Street lighting control systems enable cities and municipalities to achieve effective energy savings, reduce emissions, and enhance operational efficiency. These systems also provide additional features that improve the functionality of lighting infrastructure.
- Energy Efficiency: Control systems reduce energy consumption by up to 70% through targeted dimming and automatic adjustments.
- Remote Management: Remote control enables switching and dimming of individual or grouped streetlights, ensuring optimal illumination without manual intervention.
- Data Monitoring: Real-time collection of data such as voltage, current, and energy consumption allows for detailed analysis and timely maintenance.
- Additional Features: Integration with cameras for traffic monitoring, sensors for environmental data collection, and other smart functionalities enhance system versatility.
By adopting these solutions, cities can ensure sustainable energy use while improving the quality of life for residents.
Photocell Switch Control System

Photocell switches are one of the simplest and most widely used streetlight control solutions. They automatically turn lights on or off based on ambient light levels.
Standard Photocell Switch
- How It Works: The photocell detects changes in light intensity. When it gets dark, the resistance of the photocell increases, completing the circuit and turning the lights on. Conversely, when it becomes brighter, the circuit is broken, and the lights turn off.
- Advantages: Reduces unnecessary lighting and saves energy.
- Limitations: External factors like lightning, car headlights, or obstructions (e.g., leaves or buildings) can cause false signals, leading to operational inefficiencies.
Photocell Switch with Timing Dimming
This upgraded version integrates dimming capabilities. After the photocell turns the lights on, the system can reduce brightness at predefined times (e.g., 50% brightness after midnight). This ensures energy savings while maintaining adequate lighting during peak traffic hours.
Timing Dimming Control System

Timing dimming systems enable preprogrammed adjustments to streetlight brightness based on time schedules. This feature is particularly useful for roads with varying traffic volumes throughout the night.
Classical Timing Dimming
- How It Works: The LED driver is preprogrammed with a dimming schedule. For example, lights operate at 100% brightness for the first six hours, then dim to 50% for the remaining six hours.
- Limitations: Fixed schedules may not align perfectly with real-world traffic patterns, leading to under-illumination during busy hours.
Self-Adapting-Percentage Timing Dimming
This method dynamically adjusts the dimming schedule based on traffic trends. For instance:
- 100% brightness from 18:00 to 24:00.
- 50% brightness from 24:00 to 6:00.
This approach ensures better alignment with road usage, improving both efficiency and safety.
Self-Adapting-Midnight Timing Dimming
Often referred to as "virtual midnight dimming," this advanced feature adjusts brightness based on the average on-time of the past two days. It assumes midnight as the center point of the dimming curve, with the lowest brightness levels from 0:00 to 4:00. This reduces energy consumption significantly, especially during low-traffic periods.
| Brightness Level | Period |
|---|---|
| 100% | Sunset to midnight |
| 50% | Midnight to early morning |
| 100% | Early morning to sunrise |
Smart Street Lighting Control System

Smart streetlight control systems provide advanced functionality by integrating wireless networks, sensors, and data analytics. They allow real-time control and monitoring, making them ideal for cities aiming to implement smart infrastructure.
Features of Smart Control Systems
- Remote Monitoring: Automatically detect faults and send maintenance alerts.
- Customizable Dimming: Adjust brightness levels for individual lights or groups based on traffic or environmental conditions.
- Energy Savings: Reduce electricity usage through precise control, achieving savings of up to 70%.
- Additional Capabilities: Integrate with urban monitoring systems for traffic, security, and environmental data collection.
Comparison of Control Systems
| Control Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Time Switch | Simple and widely used | Requires manual adjustments |
| Photocell Switch | Plug-and-play, energy-saving | Prone to false triggers |
| Timing Dimming | Energy-saving without extra cost | Less flexible than smart systems |
| Smart System | Advanced functionality, real-time monitoring | High initial cost, complexity |
Summary
Streetlight control systems provide an efficient way to manage public lighting while saving energy and reducing operational costs. Key options include:
- Photocell Switches: Simple, cost-effective solutions for automatic switching.
- Timing Dimming: Preprogrammed dimming for consistent energy savings.
- Smart Control Systems: Advanced capabilities for real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustments.
While smart systems offer the most comprehensive features, combining photocell switches with timing dimming provides an affordable yet efficient alternative. By focusing on energy efficiency and operational ease, cities can ensure sustainable and cost-effective street lighting solutions.


