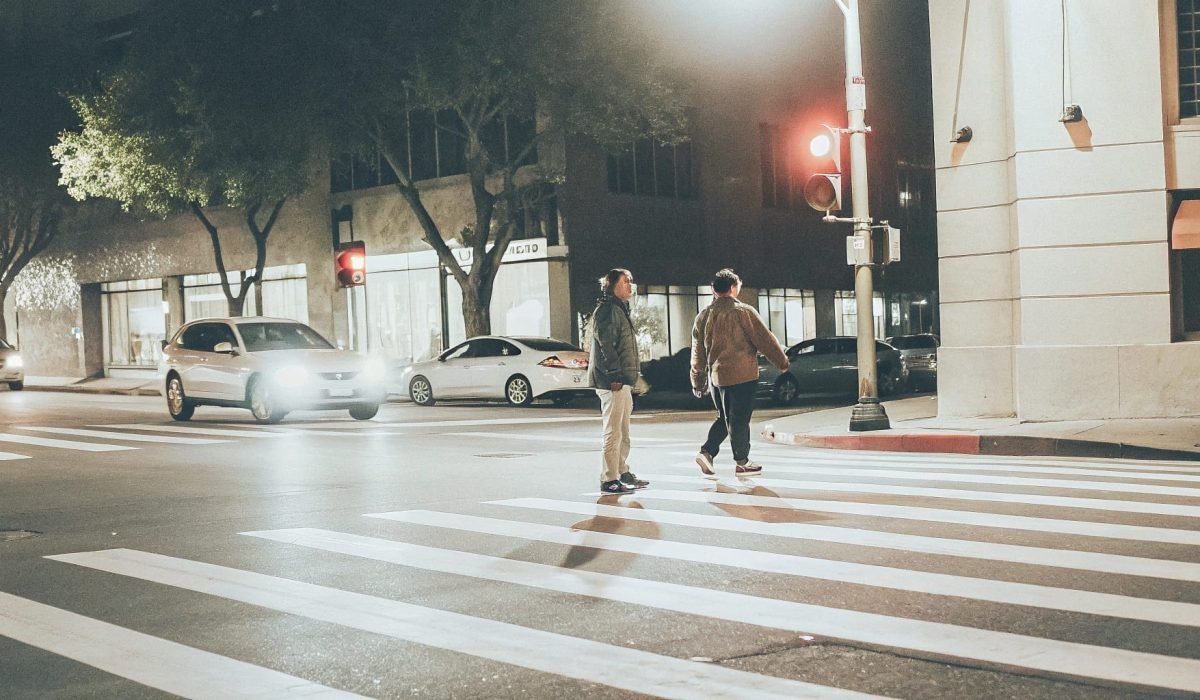
Proper pedestrian lighting is essential for road safety. It reduces nighttime accidents, improves pedestrian visibility, and supports smoother traffic flow, making urban spaces safer and more welcoming.
Effective pedestrian lighting minimizes accident risks by enhancing visibility and increasing driver awareness. It ensures safer crossings, encourages nighttime activities, and contributes to urban development.
Pedestrian crossings require specialized lighting design to maximize safety and efficiency. In this article, I’ll explore the benefits, functionality, and key considerations for pedestrian-focused lighting.
What are the benefits of pedestrian scale lighting?
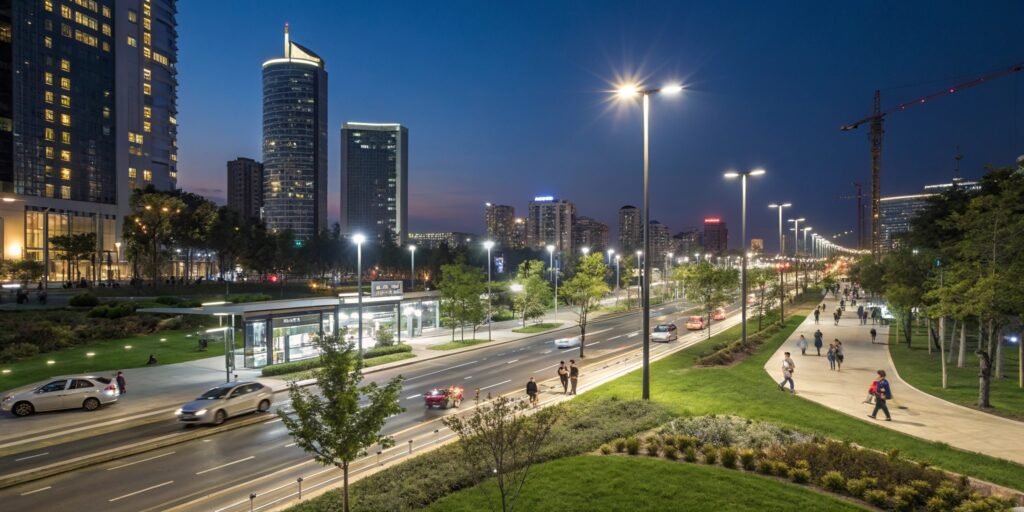

Pedestrian-scale lighting plays a vital role in modern cities. Poorly lit crossings put both pedestrians and drivers at significant risk, especially at night.
Enhanced pedestrian lighting increases safety by improving visibility for drivers and pedestrians. It creates a safer urban environment while encouraging economic and social activities.
Improved Safety
Accidents often occur at crossings, particularly in low-light conditions. High-quality lighting ensures pedestrians are visible to approaching vehicles. Drivers can react more quickly, reducing accidents. Proper lighting also makes pedestrian zones feel safer, encouraging use during the night.
Encouraging Social and Economic Activity
Well-lit areas promote evening activities such as outdoor dining, markets, and events. People feel secure in illuminated spaces, leading to increased community interaction. Furthermore, these activities boost local businesses, supporting urban economic development.
Enhancing Urban Aesthetics
Pedestrian lighting contributes to the visual appeal of cities. With thoughtful design, lighting installations can blend with urban landscapes. Improved aesthetics attract tourists, enhance property values, and foster a sense of pride among residents.
How do pedestrian crossing lights work?

Pedestrian crossing lights combine strategic placement, advanced optics, and reliable illumination to improve safety and visibility.
These lights use polarized lenses and vertical illumination to ensure pedestrians are visible to drivers from a distance. Balanced distribution reduces blind spots.
Key Features of Pedestrian Crossing Lights
-
Vertical Illumination
Vertical illumination highlights pedestrians, making them stand out against the road surface. This helps drivers recognize crossing individuals even from a distance. -
Polarized Lens Design
Polarized lenses focus light directly onto pedestrian zones. They minimize glare and prevent overexposure, ensuring a clear view of pedestrians without blinding drivers. -
Asymmetric Light Distribution
Lights are placed strategically to distribute light evenly across the crossing. This eliminates shadows and reduces blind spots. -
Energy Efficiency
Modern pedestrian lights often incorporate LED technology. LEDs provide bright, focused illumination while consuming less energy. They also have longer lifespans, reducing maintenance costs.
Standards and requirements for pedestrian lighting

International standards guide the design of pedestrian lighting to ensure effectiveness and safety in urban settings.
Standards like EN 13201-2 and DIN 67523 emphasize sufficient vertical illumination, uniform lighting, and balanced placement for effective crossings.
Key International Standards
- EN 13201-2: Recommends adequate luminance and vertical illumination for crosswalks to ensure visibility for both pedestrians and drivers.
- DIN 67523: Defines minimum vertical illuminance values and stresses uniform lighting across pedestrian zones.
Design Principles
-
Coverage and Placement
Lighting should illuminate the entire crossing and adjacent waiting zones. Place fixtures on both sides of the crossing rather than directly above. -
Uniformity
Light distribution must be even, eliminating shadows or excessively bright areas. Uniform lighting improves driver perception and reduces risks. -
Continuous Illumination
Lights should remain active throughout the night. This ensures consistent safety and reliability for pedestrians at all times.
Lighting design for different road configurations
Pedestrian lighting must adapt to varying road configurations, from narrow single lanes to multi-lane highways.
The placement of poles and choice of lens design should reflect road width, traffic patterns, and pedestrian needs. Proper customization ensures optimal visibility and safety.
One-Way Traffic – Single Lane
For roads about 3.5 meters wide, a single streetlight with a right-polarized lens can provide sufficient illumination. If the light pole is placed on the opposite side, a left-polarized lens should be used.
One-Way Traffic – 2–3 Lanes
Wider roads (around 7 meters) require two streetlights, one on each side. Combining right-polarized and left-polarized designs ensures uniform lighting, allowing pedestrians to be visible from both directions.
Two-Way Traffic – 2–3 Lanes
For two-way roads, poles should be placed diagonally to illuminate both directions effectively. Use right-polarized or left-polarized lenses based on road orientation.
Two-Way Traffic – 4 Lanes
Larger intersections demand additional lighting on central dividers. Four streetlights with polarized lenses are recommended for balanced illumination. Floodlights may also be used in conflict zones.
| Road Type | Lighting Solution |
|---|---|
| Single Lane | 1 light with a right/left-polarized lens depending on pole placement |
| 2–3 Lane One-Way | 2 lights with right and left-polarized lenses |
| 2–3 Lane Two-Way | Diagonal poles with polarized lenses |
| 4 Lane Two-Way | Central divider lighting and floodlights |
Conclusion

Pedestrian-focused lighting significantly enhances safety, visibility, and urban aesthetics. By prioritizing vertical illumination and tailored designs, cities can create safer, more vibrant spaces for both pedestrians and drivers.


