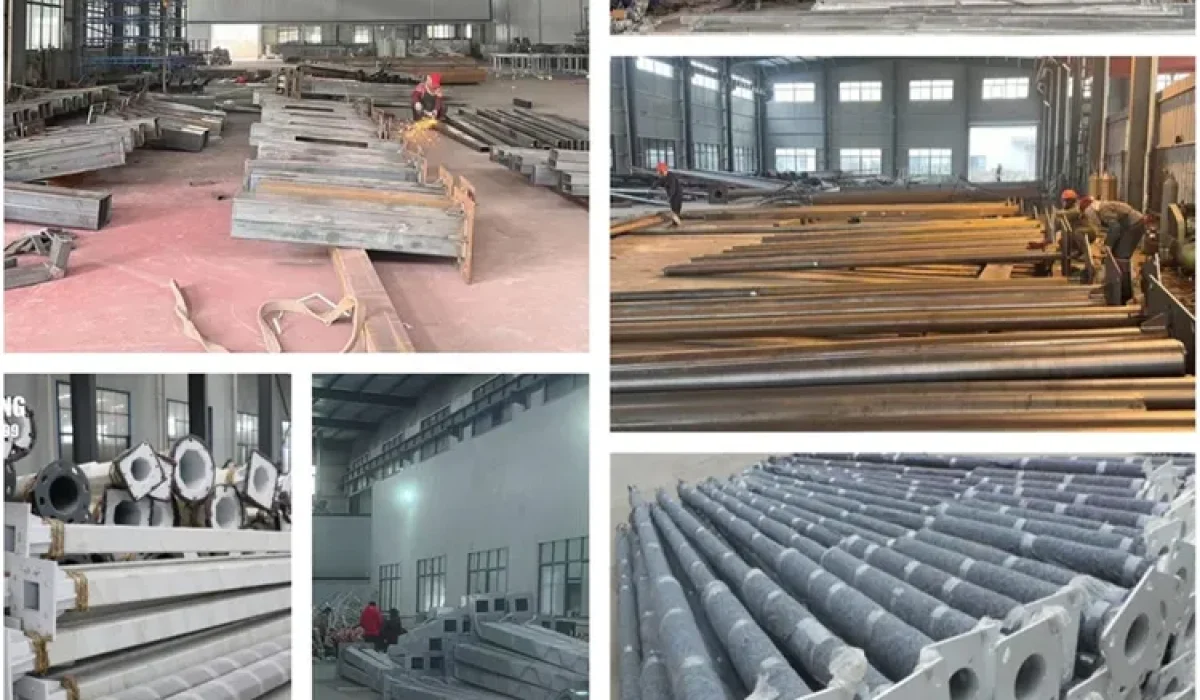
A hot-dip galvanized street light pole is a steel lighting pole protected by a zinc coating to resist corrosion in outdoor infrastructure. For EPCs and municipalities, the real decision is usually not “galvanized or not”—it’s (1) EN ISO 1461 coating thickness & sampling verification, (2) structural details (base plate, welds, anchor bolts), and (3) mounting height + spacing + optics to meet roadway illuminance and uniformity targets.
60-Second Procurement Summary (Read This First)
- Specify EN ISO 1461 and require coating thickness records by inspection lot.
- Confirm steel thickness range (it changes minimum zinc thickness requirements).
- Lock base plate + bolt circle + anchor bolt template early to avoid foundation rework.
- Request IES photometric files and a DIALux/AGi32 layout to validate average illuminance + uniformity (not “bright under the pole” demos).
- Ask for a Tender/Submittal Pack before payment: drawings, QC checklist, packing list, and warranty statement.
Why Galvanized Street Light Poles Are the Preferred Choice for Infrastructure Projects
A hot-dip galvanized street light pole is fabricated from structural steel, then dipped into molten zinc to form a protective coating. The coating acts as a barrier and slows corrosion—especially important for:
- coastal roads, ports, waterfront promenades
- high-humidity and rainy regions
- rural highways with low maintenance frequency
- urban arterials where lifecycle cost and safety matter
When Should EPC Contractors Choose Galvanized Street Light Poles?
EPC contractors and government project owners typically specify galvanized street light poles in the following scenarios:
Coastal or high-humidity regions, where corrosion resistance is critical
Infrastructure projects with a 15–25 year design life
Government tenders requiring EN or ISO compliance
Road, highway, or high-mast lighting projects with limited maintenance access
Projects prioritizing long-term lifecycle cost over low initial price
In these cases, hot-dip galvanized poles offer predictable durability, standardized quality, and significantly reduced maintenance requirements over their service life.
Typical pole types include tapered octagonal, round, or polygonal shafts, with a base plate designed for anchor bolts and a service door for wiring access.

Why Galvanizing Matters in Infrastructure Projects
For project buyers, galvanizing is about risk reduction and lifecycle cost, not just surface finish.
Common failure modes galvanizing helps prevent
- early rusting around weld seams, service doors, and base plates
- corrosion acceleration in coastal sites due to salt and high humidity
- maintenance complaints (repainting cycles, safety concerns, aesthetic issues)
Procurement reality (why “galvanized” is not enough)
Two poles can both be labeled “galvanized,” yet behave very differently in the field. That’s why EN ISO 1461 verification plus structural specs (base plate, bolts, wall thickness, wind assumptions) matter more than brochure language.
EN ISO 1461: Coating Thickness & Sampling (Project-Ready)
If your tender or BOQ only says “hot-dip galvanized,” it’s incomplete. You should specify:
1) the standard (EN ISO 1461)
2) minimum coating thickness requirements
3) how thickness is sampled and recorded
Minimum coating thickness (non-centrifuged articles)
Minimum coating thickness depends on steel section thickness (t). EN ISO 1461 uses local thickness and mean thickness requirements.
| Steel thickness interval (t) | Minimum local thickness (μm) | Minimum mean thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| t > 6 mm | 70 | 85 |
| 3 < t ≤ 6 mm | 55 | 70 |
| 1.5 < t ≤ 3 mm | 45 | 55 |
| t ≤ 1.5 mm | 35 | 45 |
Minimum coating thickness (centrifuged articles)
Centrifuged items (often small parts) have different minimum values:
| Product type | Steel thickness interval (t) | Minimum local thickness (μm) | Minimum mean thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded products | t > 6 mm | 40 | 50 |
| Threaded products | t ≤ 6 mm | 20 | 25 |
| Others | t ≥ 3 mm | 45 | 55 |
| Others | t < 3 mm | 35 | 45 |
Control sample size (inspection lot sampling)
EN ISO 1461 also defines the minimum number of articles to check in each inspection lot:
| Number of articles in the lot | Minimum number of articles in the control sample |
|---|---|
| 1–3 | All |
| 4–500 | 3 |
| 501–1200 | 5 |
| 1201–3200 | 8 |
| 3201–10,000 | 13 |
| Over 10,000 | 20 |
Tender clause template (copy & paste)
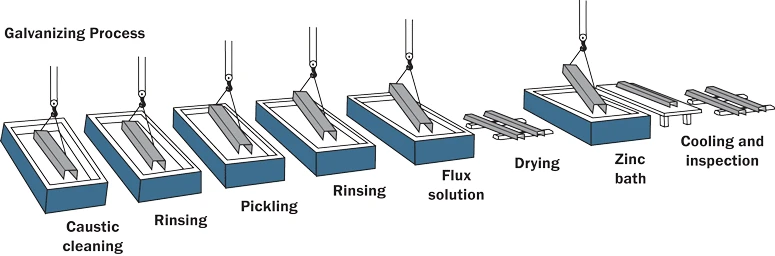
Tender Clause (Galvanizing): Hot-dip galvanizing shall comply with EN ISO 1461. Coating thickness shall meet the minimum local and mean thickness requirements for the relevant steel section thickness intervals. Thickness shall be verified using a calibrated magnetic gauge, and sampling size shall follow EN ISO 1461 control sample rules based on inspection lot size. Any damaged areas after handling or transportation shall be repaired using suitable zinc-rich materials compatible with galvanized coatings.
How to Inspect Galvanizing on Street Light Poles
A good supplier can provide a simple, auditable inspection trail.
What to check (practical steps)
- Thickness measurement method: calibrated magnetic thickness gauge
- Where to measure: avoid edges, holes, and discontinuities (non-representative points)
- Records: thickness log by inspection lot (with lot/serial identification where applicable)
What to request as proof (minimum)
- coating thickness report (local + mean) by inspection lot
- inspection lot definition and sampling plan
- photos of thickness measurement process (optional but helpful)
- packing method to reduce transport damage (especially base plate and door area)
Key Pole Engineering Specs You Should Put in a BOQ
Below is a BOQ-ready checklist for EPC and municipal procurement.
Pole geometry & structure
- pole height (m) and mounting height
- shaft type (tapered octagonal / round / polygonal)
- wall thickness range (mm)
- service door size and position
- bracket/arm type (single / double / custom outreach)
- luminaire mounting interface and access details (if required)
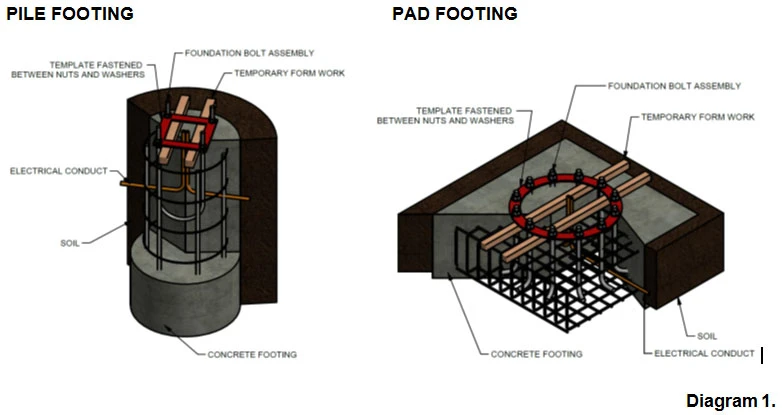
Base plate & anchor bolts (avoid foundation rework)
- base plate thickness and dimensions
- bolt circle diameter (BCD) and hole diameter
- anchor bolt size/grade/length and nut/washer set
- anchor bolt template drawing (must match foundation design)
Welding & fabrication
- weld type and inspection requirement
- straightness tolerance (project-defined)
- galvanizing after full fabrication (not before)
Quick BOQ table (copy & paste)
| Item | Specify in BOQ |
|---|---|
| Galvanizing standard | EN ISO 1461 |
| Pole height | ___ m |
| Shaft type | Tapered octagonal / round / polygonal |
| Wall thickness | ___ mm (range) |
| Base plate | mm thick, x ___ mm |
| Bolt circle | mm, holes mm |
| Anchor bolts | M x pcs, grade , length |
| Arm/bracket | outreach ___ mm, single/double |
| Submittals | drawings, thickness records plan, packing list, warranty |
Roadway Lighting Performance: Pole Height, Spacing, and Uniformity
Poles do not create lighting performance alone. Mounting height, spacing, luminaire optics, and roadway geometry determine whether you pass acceptance.
A common roadway design workflow is:
- Define illuminance/uniformity targets.
- Select luminaire distribution (IES files).
- Simulate the layout (DIALux/AGi32).
- Confirm pole height + arm outreach + spacing.
- Lock BOQ quantities and drawings.
A practical spacing check (engineering estimate)
To ensure the procurement of poles aligns with the actual lighting requirements, the following engineering formula is used to verify performance:
$$Spacing = \frac{LL \times CU \times LLD \times LDD}{E_h \times W}$$
Where:
- $LL$: Initial lamp lumens (lm)
- $CU$: Coefficient of Utilization (depends on optics + roadway geometry)
- $LLD$: Lamp Lumen Depreciation factor
- $LDD$: Luminaire Dirt Depreciation factor
- $E_h$: Average maintained illuminance target (lux)
- $W$: Roadway width to be lighted (m)
Note: This is an engineering estimate and must be confirmed with photometric simulation (IES + layout report), especially for different roadway types and distributions.
Uniformity: what acceptance actually checks
Uniformity ensures there are no "dark spots" between poles that could compromise safety. The simple definition used in roadway practice is:
$$Ur = \frac{E{avg}}{E_{min}}$$
Where:
- $E_{avg}$: Average maintained illuminance
- $E_{min}$: Minimum maintained illuminance (typically at the midpoint between poles)
What to request from suppliers (to avoid rework)
- IES photometric files for the exact luminaire model and wattage.
- A DIALux/AGi32 report showing average illuminance and uniformity.
- Drawings confirming mounting height, outreach, tilt, and spacing.
- Wind-load notes for pole + arm + luminaire “sail area” assumptions.
Galvanized vs Painted vs Stainless Steel Poles
This is not “which is best,” but “which fits the site and maintenance plan.”
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461)
Best for:
- coastal/high-humidity/rainy regions
- low-maintenance road networks
- long-life municipal assets
Painted steel (including powder coating)
Best for:
- appearance-focused urban areas (when the coating system is specified correctly)
- projects with regular maintenance cycles
Risk:
- poor surface prep and coating system mismatch can fail early if not controlled.
Stainless steel
Best for:
- specific high-corrosion niches where budget allows
Trade-off:
- higher material cost and different fabrication considerations.
Case Study: Coastal Project Failed in 3 Years (What the Tender Missed)
A coastal roadway project specified “hot-dip galvanized poles” but did not define EN ISO 1461 thickness verification or sampling records. The supplier delivered poles with inconsistent coating thickness, and several units showed early rust around the base plate and service door after multiple rainy seasons.
What should have been specified
- EN ISO 1461 compliance + minimum local/mean thickness targets
- inspection lot sampling size and thickness records by lot
- handling/packing requirements to protect base plates and edges
- a repair rule for transport damage using compatible zinc-rich materials
Result
The project faced repainting and pole replacements earlier than planned, increasing lifecycle cost and triggering site acceptance disputes.
Applications in Infrastructure Projects
Hot-dip galvanized poles are commonly used in:
- urban arterial roads
- highways and rural roads
- industrial parks and logistics zones
- ports, coastal roads, waterfront promenades
- airports and transport hubs (site-specific)
Choosing the Right Galvanized Street Light Pole
Use this checklist to select the right pole for your project.
Step 1: Confirm environment & maintenance assumptions
- coastal vs inland
- rainy season intensity and humidity
- maintenance frequency and site access
Step 2: Lock the foundation interface
- base plate size and thickness
- bolt circle and anchor bolt grade
- anchor bolt template drawing
Step 3: Confirm lighting performance inputs
- mounting height and spacing target
- luminaire optics (IES)
- illuminance and uniformity targets
Step 4: Require verification documents
- EN ISO 1461 thickness verification plan (local + mean)
- inspection lot sampling plan
- packing list and protection method
Price & Supplier Insights (What Really Drives Cost)
In real projects, pole price is driven by:
- steel weight (height + wall thickness + base plate)
- fabrication complexity (arms, brackets, doors)
- galvanizing bath capacity and process control
- QC requirements and documentation workload
- packaging method (especially for base plates and long-distance shipment)
What usually does not predict lifecycle performance:
- a “thicker-looking” zinc finish in photos
- generic “anti-rust” phrases without EN ISO 1461 verification
Tender & Submittal Pack (What to Request from Suppliers)
Before you pay a deposit, request a tender/submittal pack.
Minimum pack contents
- pole drawing (height, taper, wall thickness, door size, bracket details)
- base plate drawing + bolt circle + anchor bolt template
- EN ISO 1461 thickness requirements + inspection records plan
- steel material certificate / traceability (as required)
- QC checklist (welding, dimensions, coating inspection)
- packing list + container loading plan (if relevant)
- warranty statement (terms and exclusions)
Optional but valuable
- factory inspection photos/videos
- sample thickness measurement photos
- reference projects in similar climates
Download (Lead Magnet): Tender Checklist PDF
If you want to speed up procurement and reduce disputes, turn this page into a PDF pack:
- EN ISO 1461 tender clause (copy & paste)
- coating thickness tables (local/mean)
- inspection lot sampling table
- BOQ spec checklist (pole + base plate + anchor bolts)
- supplier submittal checklist (docs before payment)
Download the Tender Checklist (PDF)
Internal Links (Recommended)
To build topical authority, link this article to related project pages:
- Anchor bolt template for lighting poles: /anchor-bolt-template/
- Wind load design for street light poles: /wind-load-design-lighting-poles/
- Powder coating vs galvanizing for coastal projects: /galvanizing-vs-powder-coating/
- High mast lighting poles: /high-mast-lighting-poles/
- Steel pole manufacturing & QC: /manufacturing-qc/
- Roadway lighting layout (IES + DIALux): /roadway-lighting-layout/
FAQ
How long does a hot-dip galvanized street light pole last?
Under normal outdoor conditions, a hot-dip galvanized street light pole can last 20–30 years without major maintenance.
Actual service life depends on coating thickness, environmental corrosivity, and compliance with standards such as EN ISO 1461.
What should I specify for galvanizing in a BOQ?
At minimum: EN ISO 1461, steel thickness interval, coating thickness verification, sampling size by lot, and repair requirements for transport damage.
Why do some galvanized poles rust early?
Common reasons include insufficient thickness verification by lot, poor fabrication/weld handling before galvanizing, damage during transport at edges and base plates, or lack of proper zinc-rich repair for damaged areas.
Is thicker zinc always better?
Not automatically. The key is meeting EN ISO 1461 minimum local and mean requirements and verifying thickness with the correct sampling plan. Handling controls and repair of damaged areas are equally important.
Do I need IES files if I’m only buying poles?
If luminaires are part of the supply, yes. Roadway acceptance depends on average illuminance and uniformity, so spacing and mounting height should be verified using IES photometric files and a DIALux/AGi32 layout.
Conclusion & Call to Action
A hot-dip galvanized street light pole becomes a long-life infrastructure asset when two things are done correctly:
1) EN ISO 1461 coating thickness + sampling verification is documented and traceable
2) Pole structure + base plate + anchor bolts are coordinated with lighting layout and foundation design
Request the Pole Specification & Tender Pack
Send your:
- pole height
- arm type (single/double, outreach)
- project location (or wind speed)
- bolt circle requirement
We will reply with a BOQ-ready pole spec pack, base plate drawings, and an EN ISO 1461 inspection checklist.
Author & Technical Review
Written by: Sunlurio Engineering Team
Focus: Pole specifications, galvanizing inspection, and tender submittals for EPC and municipal projects
What we can provide: EN ISO 1461 thickness records, pole drawings, anchor bolt templates, packing lists, and site acceptance checklists
Suggested link: Engineering Capability: /engineering-team/
LinkedIn: YOUR-LINKEDIN-URL


